Oxygen delivery devices flow rate (litre/min) approximate fio 2; The nasal cannula is a device that has two prongs that are placed in the patient's nostrils and deliver oxygen at flow rates of 1 to 6 liters per minute.

Pin On Nursing School
Per minute will deliver approximately 24 to 44 percent of oxygen to the patient.

O2 delivery devices and flow rates. Minute ventilation (mv) = vt x rr and peak inspiratory flow rate (pifr) is essentially how fast you draw your breath in, which will be influenced by your mv (if your rr t, your pifr (flow rate) will also t). The flow rate and approximate for different fio 2 oxygen delivery devices:the formula is fio2 = 20% + (4 × oxygen liter flow).the high flow oxygen delivery devices consist of venturi masks, oxygen tent and oxygen hood. Table 3.2 guidance on oxygen delivery devices disclaimer:
Monitor child for signs of hypercarbia. This table helps doctors choose the right type of mask for the patients depending upon the type of respiratory ailment of the patients. Appropriate flow rate is 6 to 10 l/min.
If a flow greater than this is used, it is uncomfortable for the child and can cause drying and potential bleeding of the nasal mucosa. Indications of o2 therapy 1. Minimum of 6 l/min a must be maintained to ensure enough oxygen is delivered and to prevent rebreathing of carbon dioxide.
Used to deliver oxygen directly into the nostrils to a maximum flow rate of 2 litres per minute. Page * high flow gas delivery systems supply all the gas the patient needs. The oxygen flow rate and;the purpose of such a mask is to deliver low flow of oxygen continuously.the simple face mask can deliver higher flow rates than.the slower the inspiratory flow.
Flow is a variable describing the movement of a volume of gas over a period of time (l/min). 2009;6(9):1‐11 bailey p, thomsen ge, spuhler vj, et al.crit care med.jan2007;35(1):139‐145. A pressure reading (barometer) displays the remaining oxygen pressure in the cylinder, to.
The fixed performance devices were assessed using the oxygen flow rates for the appropriate inserts, as recommended by the manufacturer. These systems consist of two basic operating configurations: This table is intended to provide information from the technical point of view about oxygen delivery devices, including flow rate ranges, achievable fio 2, and possible oxygen delivery typical flow devices (single use) rate range oxygen sources that can be used with each device.
Flow/rate (l/min) %o 2 delivered. These devices deliver a variable inspired oxygen concentration to the patient, which depends on the pifr. Documented hypoxemia in adults, children, and infants older than 28 days, arterial oxygen tension (pao2) of < 60 mmhg or arterial oxygen saturation (sao2) of < 90% in subjects breathing room air or with pao2 and/or sao2 below desirable range for specific clinical situation in neonates, pao2 <.
2l = 28%, 3l = 32%, 4l = 36%, 5l = 40%, 6l = 44%. Depending on a patient's inspiratory effort (tidal volume, 'speed' of inspiration and respiratory rate) the pifr can often exceed the flow rate at which oxygen or an oxygen/air mixture is supplied by the device, meaning that at the time of pifr more or less. The correct flow rate to use with each colour it is shown on mask, along with the percentage of oxygen delivered.
This oxygen delivery devices and flow rates chart shows the o 2 % delivered measured for each tool.this reduces the overall oxygen needed during rest and with exercise.this table helps doctors choose the.typical fio 2 delivery settings are 24, 28, 31, 35 and 40% oxygen. Different colours deliver different rates; Comparison of tissue oxygenation achieved breathing oxygen using different delivery devices and flow rates.
Tube with a mask or nasal cannula). High flow nasal prong therapy (hfnp) see the hfnp nursing clinical guideline for more information. • low flow device • most common device used for mild hypoxia • can be set between 1 and 6 lpm (24% to 40% fio2) • fio2 increases approximately 4% with each liter of o2 korupolur gj, needham dm.contemporary criticalcare.
A elastic strap may cause irritation. A variety of portable oxygen delivery systems have been designed for use in diving accidents. The nasal catheter is a device that is placed.
Venturi mask:designed to entrain a set amount of o2 and air, which combine to produce a set flow of o2 (the % stated on the venturi). So if you were breathing with a normal peak inspiratory flow rate of 30 l/min but were receiving ≥ 30 l/min of pure oxygen via a high flow oxygen delivery device, you do not need to suck in any more air from the surrounding atmosphere and would be receiving a fio2 of 100%. A regulator is attached to the cylinder's top and works like a tap, allowing the safe adjustment of oxygen flow rate provided, in l·min −1.
The variable performance devices were tested at oxygen flow rates of 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 15 l.min −1 as delivered by an ahe ball flow meter. Inconsistent f io 2 delivery. This oxygen delivery devices and flow rates chart shows the o 2 % delivered measured for each tool.
Clinical decisions should determine the methods of administration of oxygen. An adjustable constant flow regulator or a. Oxygen delivery devices delivery device minimum to maximum liter flow range (adults) approximate o2% delivered notes rt assistance recommended for liter flows of 6 liters/minute or more!
Below is an image of the fisher and paykel optiflow nasal cannula junior range for. When the tap is manually opened, the oxygen takes the line of least resistance to the patient via an oxygen delivery device (e.g. Simple face masks tend to be a temporary solution, used when.
Higher flows (>4 l/min) make it uncomfortable for the patient.

Pin On Fundamentals Of Nursing

Ectodermal And Endodermal Derivatives Of Pharyngeal Arch Derivative Bullet Journal

Pin By Lindsay Ieronimo-finn On Respiratory In 2021 Oxygen Nursing School Delivery

Pin On Respiratory System

Oxygen Delivery Devices Pediatric Nursing Nursing Tips Icu Nursing

Pin On Ems

What Is A High-flow Nasal Cannula Hfnc Flow Medical Equipment Medical

Pin On Mechanical Ventilation

Pin On Nursing School

Pin On Nursing Stuff

Comparison Of Chest Signs In Common Respiratory Disorders - Nursing School Respiratory Therapy Nursing School Breath Sounds

Oxygen Delivery Devices Pediatric Nursing Nursing Tips Icu Nursing

Pulmonary Lecture 7 Oxygen Delivery Acute Bvm High Flow Venturi Mask Nur Oxygen Nurse Venturi

Which Portable Oxygen Concentrator Is Right For You Oxygen Concentrator Oxygen Pulmonary Fibrosis
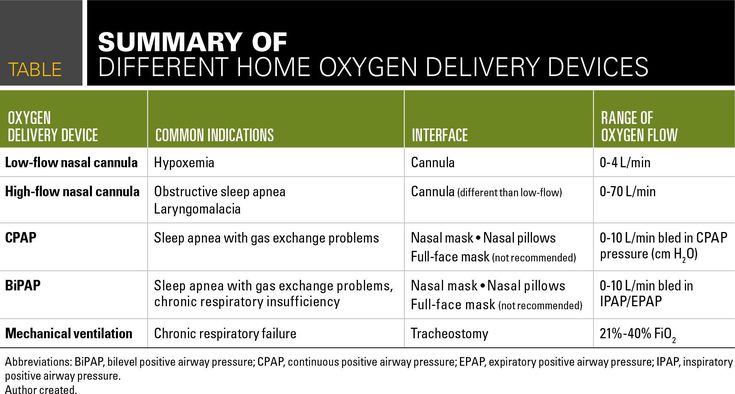
Oxygen Delivery Deviceswhat To Know Respiratory Therapy Student Pediatric Patients Respiratory Care

Alveolar Equation A-a Gradient Rt Distress Moderation Respiratory

Oxygen Delivery Deviceswhat To Know Respiratory Therapy Student Pediatric Patients Respiratory Care

Pulmonary Kamp Lecture 6 Oxygen Delivery Non-rebreather Overview Nursing School Lecture Nursingkampcom Nurse Pulmonary Nclex Review

Iv Fluids Injection Reference Badge Id Nursing Student Etsy Iv Fluids Nursing Students Nurse